Formatting Ticket Faces
- Double click on a line to open up the Ticket Face Detail window.
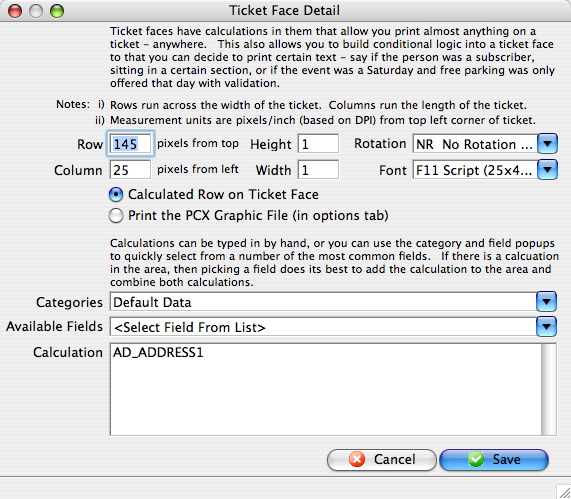
- Change the row parameter.
- Click the Save
 button.
button.
The changes have now been accepted for this line.
- Click the Test Ticket
 button.
button.
A sample ticket will print for review.
Row Placement
When you are formatting ticket faces, you need to think in Rows and Columns.
Row
The number of rows on a ticket face is dependent on the resolution of the ticket printer in dots per inch (DPI). The total number of rows is equal to the total number of dots that could be printed in the height of the ticket. To calculate the total number of rows available, multiply the DPI of the ticket printer, times the height of the ticket. For example:
- If a printer has 200 DPI resolution, it prints 200 dots
per inch. A two inch high ticket will have 400 dots or rows.
By entering 300 into the row perimeter, you instruct the printer to start printing the information at the 300th dot, or 1.5 inches from the top of the ticket.
- If the printer is 100 DPI there are 200 dots
in the height.
By entering 150 in the row parameter, you instruct the printer to start printing the information at the 150th dot or 1.5 inches from the top of the ticket.
Column Placement
- If the printer has 200 DPI resolution, it prints 200
dots per inch. A 5 inch wide ticket will have 1000 dots or columns.
By entering 300 into the column parameter, you instruct the printer to start printing the information 1.5 inches from the left edge of the ticket.
- If the printer is 100 DPI there are 500 dots in the
width.
By entering 150 in the column parameter you instruct the printer to start printing the information 1.5 inches from the left edge of the ticket.
Font Name
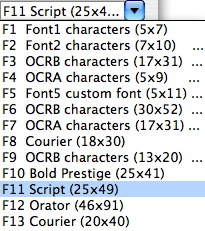
Beside the name of the font, there is a number bracketed number. This refers to the number of dots (or pixels) in each character.
A (5 x 7) font means that the font is designed to print each character 5 dots wide and 7 dots high on the ticket face.
You can alter the size of the font by changing the height or width parameter in the ticket face to make it bigger in one or both directions.
Font Height
For example:
- if the font selected is (5 x 7) pixels -and-
- the height set at 4
Font Width
For example:
- if the font selected is (5 x 7) pixels -and-
- the width set at 2
Font Rotation
The options are:
- NR (No Rotation) means no rotation and information is printed horizontally along the ticket face.
- RL (Rotate 90+) means rotate the text clockwise (to the left) and print from the top to bottom.
- RR (Rotate 90-) means rotate the text counter clockwise (to the right) and print from the bottom of the ticket to the top.
- RU (Rotate 180) means print the text upside down on the ticket face.
Note: the row and column settings indicate where the text starts to print. If you are printing using the rotation RR from bottom to top, then you may wish to have a row that is near the bottom of the ticket (and vice versa for RL)
Calculation on Ticket
Both methods can be used to build a ticket. Available fields are divided into several groups.
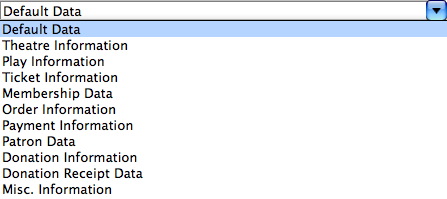
| Default Data | Enables the placement of information about the company contained in the Company Preferences setup. For example, the company name, address, and telephone numbers. | ||
| Theatre Information |
|
||
| Play Information | Enables the placement of information about the Plays and Dates associated with the ticket. For example, the play title, play date and time, and play sponsor. | ||
| Ticket Information |
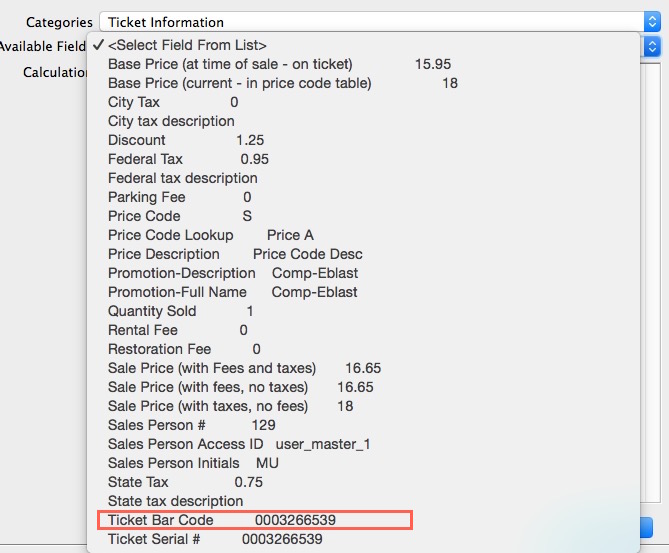 Enables the placement of information about the ticket sold to the patron. For example, the price paid, price discounts, and the ticket serial number. The ticket serial number is a unique number generated by Theatre Manager for each ticket.
Enables the placement of information about the ticket sold to the patron. For example, the price paid, price discounts, and the ticket serial number. The ticket serial number is a unique number generated by Theatre Manager for each ticket.
The unique number can be printed on any ticket along with the ticket bar code field in ladder format as shown in the picture or as a QR code if using Microcom printers. All you have to do is select the bar code and make sure it prints clearly and entirely on the ticket (but not on a perforation). Some interesting ticket calculations:
|
||
| Pass/GC/Member Data |
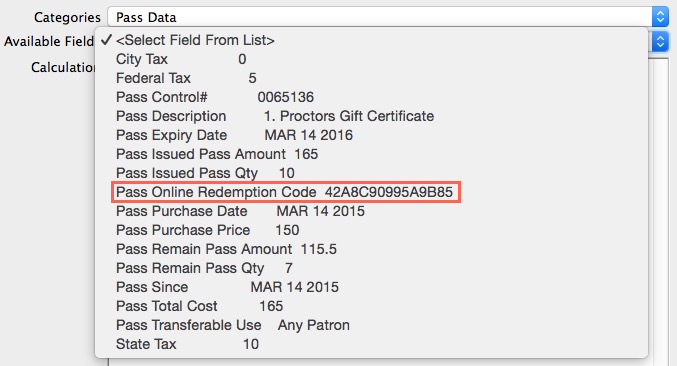 Enables the placement of information about the pass, gift certificate, or membership
sold to the patron. For example, purchase date, expiry date, member type, control number, and online redemption password.
Enables the placement of information about the pass, gift certificate, or membership
sold to the patron. For example, purchase date, expiry date, member type, control number, and online redemption password.
|
||
| Order Information | Enables the placement of information about the order created when the ticket was sold to the patron. For example, the order date and total order dollar amount outstanding. | ||
| Payment Information | Enables the placement of information about the payment made by the patron. For example, payment type, total payment value, and the credit card number. | ||
| Patron Information | Enables the placement of information about the patron. For example, the patron name, address, and telephone numbers. | ||
| Donation Information | Enables the placement of information about the donation made by the patron. For example, the campaign, donation date, and the total donation amount outstanding. | ||
| Donation Receipt Data | Enables the placement of information about the donation receipt as it pertains to donation of a patron. For example, the receipt number, date the receipt was issued and the value of the receipt. | ||
| Miscellaneous Information | Enables the placement of printer created information. For example, drawing boxes, drawing lines, and printing the internal ticket printing counter. The internal ticket printer number is a number generated by the printer every time a ticket is printed. If the same ticket is printed 4 times, each ticket will have an unique number. |
Calculation Commands
|
Quick reference information for Calculation Commands |
 |
Calculation commands are great if you know the name of the field and you want to manipulate it.
However, sometimes you may need to add a new field from a pick list in order find the name of what you want. |
The third line of the sample screen C_HOME_PHONE has no formatting in the field calculation.
This instructs the printer to left justify the home phone of the patron starting in row 15 and column 1040. To justify the phone number place the field in brackets and prefix it with the letters 'jst'. Follow the field (inside the bracket) with a comma and a single quote to start the formatting instructions, enter the formatting instructions, and close with a single quote.
For example, jst(C_HOME_PHONE,'-8') formats the field calculation to allocate 8 spaces for the home phone number and to right justify when printing.
String Justification
| String | Description | Example |
| jst () |
jst(string1,number1,string2,number2,string3,number3,...) Returns a string containing the specified string left or tight justified with sufficient spaces added to make a total length specified by number. The jst() function also includes concatenation. If number is negative the resulting string is right justified, if the number is positive the string is left justified; number must be in the range of 1 to 999. |
|
| ^n | (caret) Causes the data to be centered in the field n characters wide. |
|
| -n | (minus) Causes the data to be right justified in a field n characters wide. |
|
| $ | Places a $ sign in front of the data. |
|
| Pc | Causes the part of the field not filled by the data to be filled by character c. |
|
| X | Causes the data to be truncated if its length exceeds the field length. The default is not to truncate. |
|
| U | Causes the data to be converted to upper case. |
|
| L | Causes the data to be converted to lower case. |
|
| C | Causes the data to be capitalized. |
|
| Nnn | Causes the data to be treated as a fixed decimal number with nn decimal places. |
|
| E | Applies to numbers only and displays a blank when the number is zero. |
|
| , | Applies to numbers only and adds commas as number separators. |
|
String Functions
| String | Description | Example |
| cap() |
Returns the capitalized representation of a string, that is, the first letter of each and every word in the string is capitalized. |
|
| con(string1, string2, [,string3] ...) |
Returns a string concatenating or combining two or more string values.
Theatre Manager will build concatenations. Simply select more than one field from the available fields list when editing the field calculation. To format the concatenation simply treat the concatenation as one field calculation. |
First name, address, and postal code information together on the same line and places a slash between each item. Formatting is limited to the group of fields linked together.
Centers section, row, and seat number in a space 38 characters wide. A comma and row precede the row number and separate it from the actual number. A comma and seat precede the seat number and separate it from the actual number.
Prints 'Saturday, December 21 1998 Time: 8:00 PM'. The printing would be centered in a 50 character space. |
| len() | Returns the length of the string, that is, number of characters. |
|
| low() | Returns the lower case representation of a string. Any non-alphabetic characters in the strings are unaffected by low(). |
|
| mid( string, position, length) | Returns a substring of a specified length, starting at a specified position, from a larger string. If position is less than 1 it is taken as 1, that is the first character; if it is greater than the length of the string, an empty string is returned. If length is greater than the maximum length of any substring of string starting at position, then the returned substring will be the remainder of string starting at position.. |
|
| pos(substring, string) | Returns the position of a substring within a larger string. The substring must be contained within string in its entirety for the returned value to be non-zero. |
|
| upp() | Returns the upper case representation of a string. Any non-alphabetic characters in the strings are unaffected by low(). |
|
| tStringFields.$splitString( String1, width, segment) |
Returns the Nth segment from the string string where the string is broken into even word boundaries that are no no longer than width.
CR's LF's, Tabs are converted to spaces and double spaces are then removed from within the string. |
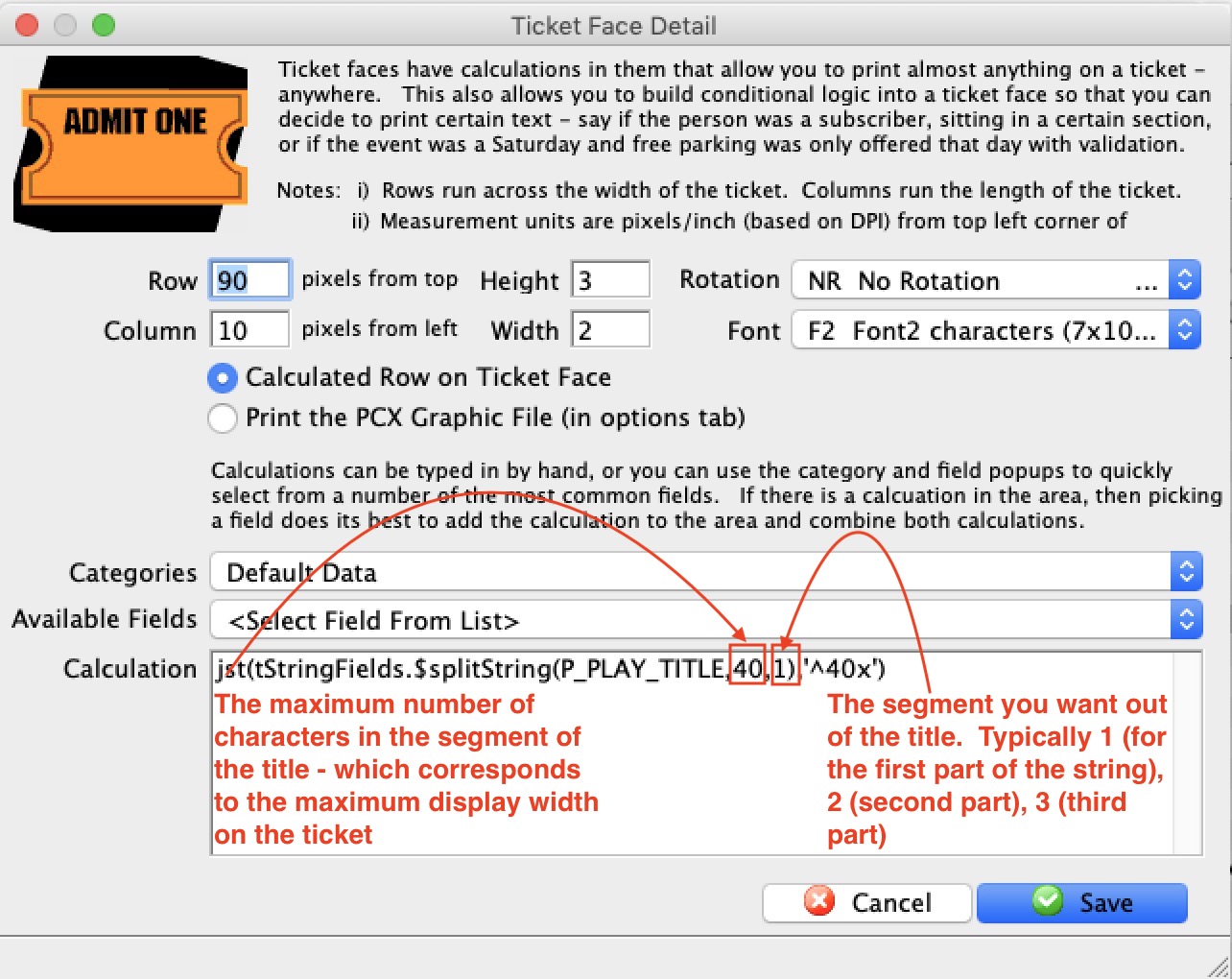 example: tStringFields.$splitString(P_PLAY_TITLE,1)
example: tStringFields.$splitString(P_PLAY_TITLE,1)
will take a long string like P_PLAY_TITLE and find entire words within the width of 40 characters and return only those. eg, for a title like:
|
| tTicket.$getReceipt( Pixels) | Prints a Moneris EMV receipt on the ticket printer using the font and rotation indicates. The receipt starts printing at the row and column specified. Each successive line will be separated by the number of DPI in the parameter. |
|
Date/Time Functions
The date/time functions operate on a datestring to return date values or strings representing some part of a date/time. A datestring is a string recognizable as a date using a date format.
| String | Description | Example |
| dat(datestring| number [,dateformat]) |
Converts a datestring or number to a date value using a second optional argument, a dateformat string. The date formatting string can be composed of the following symbols:
|
|
| dim(datestring,number) |
Increments a datestring by a number of months. Months containing different numbers of days are accounted for. Jan 31 96 increased by one month gives Feb 29 96, but beware, Feb 29 96 decreased by one month (using a negative number) returns Jan 29 96, not Jan 31 96. |
|
| dtcy(datestring) |
Returns the year and century of a datestring as a string. |
|
| dtd(datestring) | Returns the day part of a datestring unless it is part of a calculation when it is returns as a number. |
|
| dtm(datestring) | Returns the month part of a datestring. |
|
| dtw(datestring) | Returns the week part of a datestring. |
|
| dty(datestring) | Returns the year part of a datestring. |
|
| tim(timestring[,timeformat]) |
Converts a timestring to a time value using a second optional argument, a timeformat string. The time formattinG string can be composed of the following symbols:
|
|
Lookup Functions
The lookup functions provide a method for selecting items from a list of values.
| String | Description | Example |
| max(value1[,value2]...) |
Returns the maximum value from the list of values. The values should all be numbers when numeric comparison is used or all strings when string comparison is used. |
|
| min(value1[,value2]...) | Returns the minimum value from the list of values. The values should all be numbers when numeric comparison is used or all strings when string comparison is used. |
|
| pick(number,value0,value1,[value2]...) |
Selects an item from a list of string or numeric values. The number argument is rounded to an integer and used to select the item. value0 is returned if the result is 0, value1 if the result is 1, value2 if the result is 2, and so on. If the number is less than zero or greater than the number of values in the list, then an empty value is returned. The list of values can be a mixture of string and numeric values. |
|
Number Functions
| String | Description | Example |
| abs(number) |
Returns the magnitude of a real number ignoring its positive or negative sign. |
|
| int(number) |
Returns the integer part of a number; it does not round to the nearest integer. |
|
| mod(number1,number2) | Returns the remainder of a number division, that is, when number1 is divided by number1 to produce a remainder; it is a true modulus function. |
|
| rnd(number,dp) |
Rounds a number to a specified number of decimal places by dp . |
|
Labels
Entering a label, or string of characters that will be the same on every ticket, is accomplished by placing the label in single quotes.
Ontario Face Value Requirements for Ticket Price
- The content of the 'Fave Value' of a ticket is set up in Company Preferences->Ticket Options
- For e-tickets, the display of the face value is enabled in the Web Options Tab. if set, then print at home tickets and web carts will automatically show the face value along with final price.
- There is a ticket face calculation (illustrated below) that calculates the Face Value for the ticket face prior to printing it. All you need to do is include it on your ticket faces. where desired
Adding Face Value field to a ticket face
- add a new calculation to the ticket face
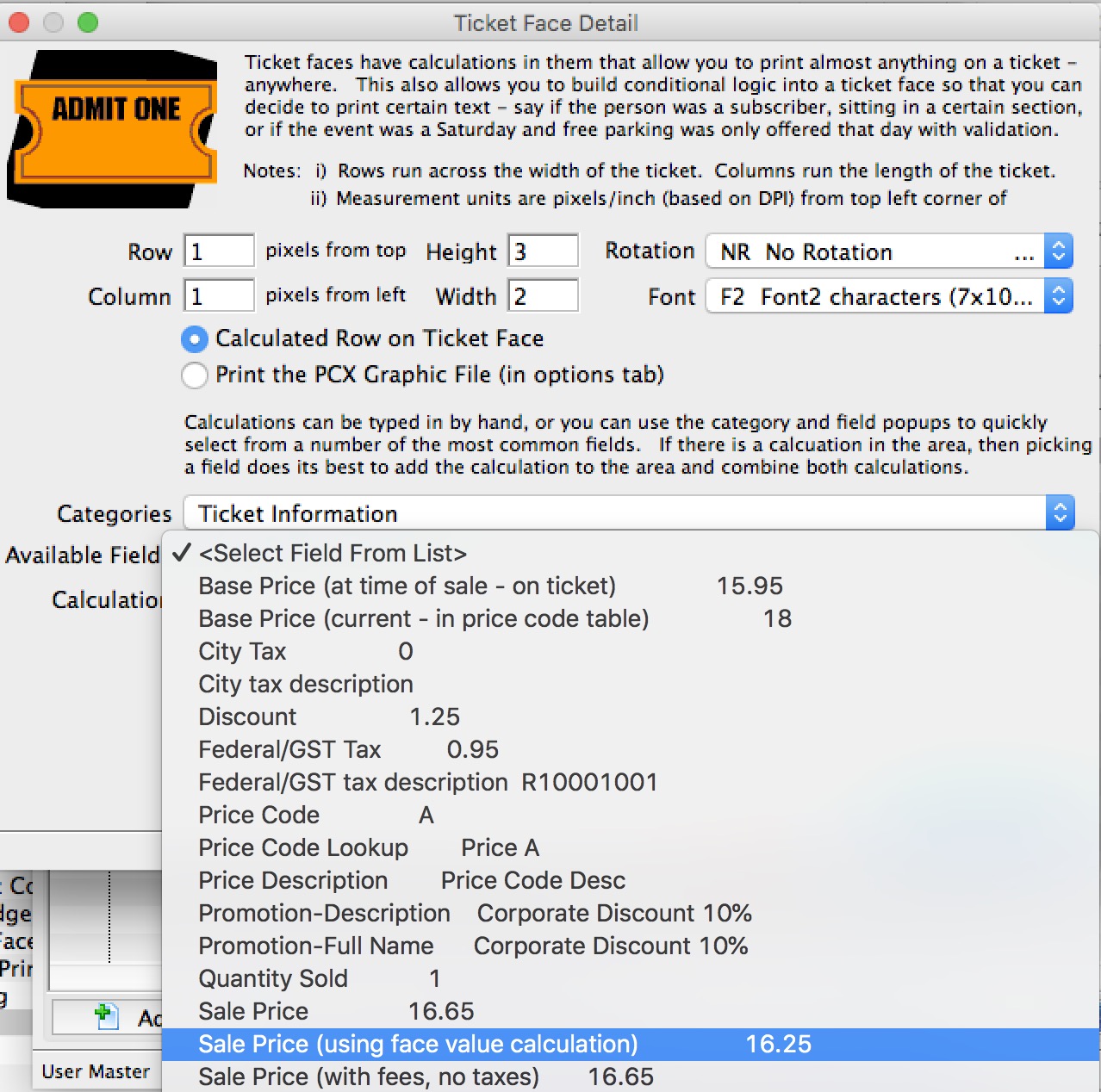
- Select Ticket Information as the category
- Select Sale Price (using Face Value calculation) to insert the field into the ticket face
- Place the face value field where you want it on the ticket and save
- Make sure to test your ticket
- Repeat for all affected tickets.
QR Codes and Printer Compatibility
 |
As of September 2021, we are aware of two ticket printers that can print QR codes on the ticket face:
|
 |
Practical Automation does not support QR codes at time of writing and older printers are not field upgradeable. |
Sample Ticket with QR code
Inserting QR code into a Ticket Face
To add a QR code to a ticket face, you need to make sure that the area yo want to print it on is big enough and is high contrast.. Usually that means an ALL-WHITE stub area. If the area you chose to print the QR code on has darker coloured background you may find scanning times increased.
The steps are:
- Insert a new calculation line in your ticket face.
- Select Ticket Information from the Categories field
- Select QR code from the Available Fields in the image to the right.
- That will add the correct calculation to your ticket face as per the image below

If you are using a Boca printer you will need to update the default QR code with additional characters. Where the default code looks like: con('<QR6,1,1,2>ticket=',PS_SEQ,'~010patron=',PS_C_SEQ,'~010')
backets will need to be added to the con statement following the QR references to make the code look like this:
con('<QR6,1,1,2>{ticket=',PS_SEQ,'~010patron=',PS_C_SEQ,'~010}')
- Change the Column to about 890 or so - so that it prints on the stub. The ticket example above uses 890 in the ticket face code shown in the next diagram.
- The Row might need to be adjusted a little to move the QR code away from the edge of the ticket and center it across the narrow part of the ticket. The ticket example above uses 100 in the ticket face code shown in the next diagram.
- You may need to remove some of the other fields that are on the stub area of the ticket face
- Test the ticket face with QR code
- Do a test print to see that it works
- Do a test scan of the ticket using your scanners to see that it works. Working only means that the scan is successful and that the ticket will likely be rejected as not being sold, or not for this day, etc
- Adjust the ticket face as necessary and reprint and retest
Sample QR Code from the above ticket exmaple
Explaining the QR code format
<QR#,#,#,#>{barcode text}
NOTE: You should not change the parameters in the QR code without talking to AMS support. Only adjust the position of the QR code on the ticket face using the Row and Column settings.
All of the Quick Response (QR) bar code command parameters are optional. If omitted default values will be used. The QR command and the barcode text is all that is required. For example the command
The Parameters, explained in order, are:
1 is the default for Theatre Manager and is required
Point size
we have found that '4' to '6' are suitable sizes for a bar code on a ticket stub
Apply Tilde
When Apply Tilde is equal to 1, the tilde (~) may be used to recognize some special characters in the input data.
Encode Mode
The data represented in the symbol may be compressed by changing the encoding mode, if certain text is being encoded. Valid values are:
Error Correction
The level of Reed Solomon error correction level placed in the symbol. More error correction creates a larger symbol that can withstand more damage. Valid values are:
{barcode text}
Do not change any values in this - otherwise ticket scanning will not work.
QR Code for Scanning Gifted Tickets
Scanning tickets that have been gifted to another patron in the database require the gifted patron number be included in the QR code inserted on the Ticket Face. The existing ticket face with a QR code can be updated to include the gifted patron number:
- Open the existing Ticket Face that has a QR code
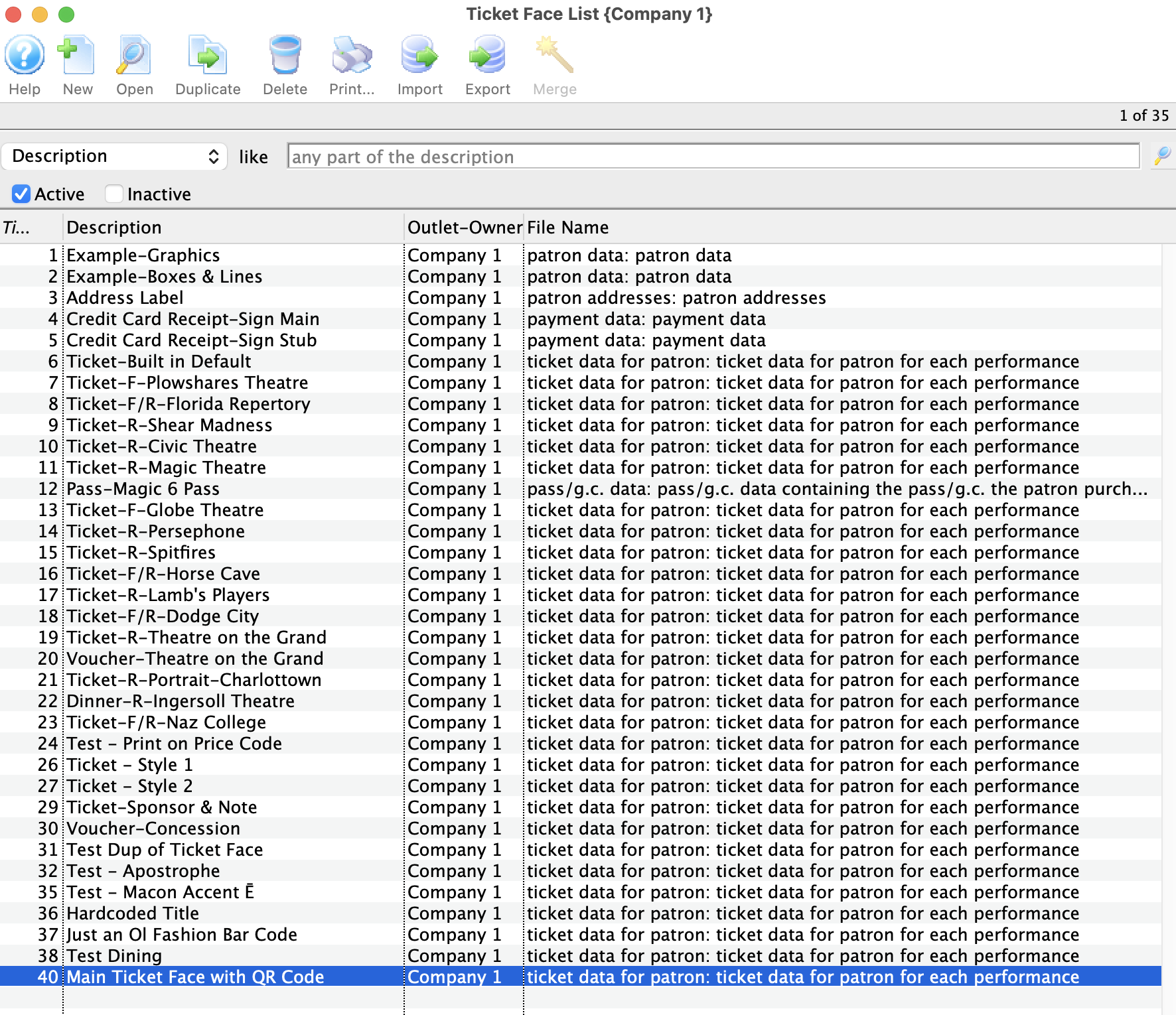
- Locate the line of code in the Ticket Face that looks like this:
con('<QR6,1,1,2>{ticket=',PS_SEQ,'~010patron=',PS_C_SEQ,'~010}')
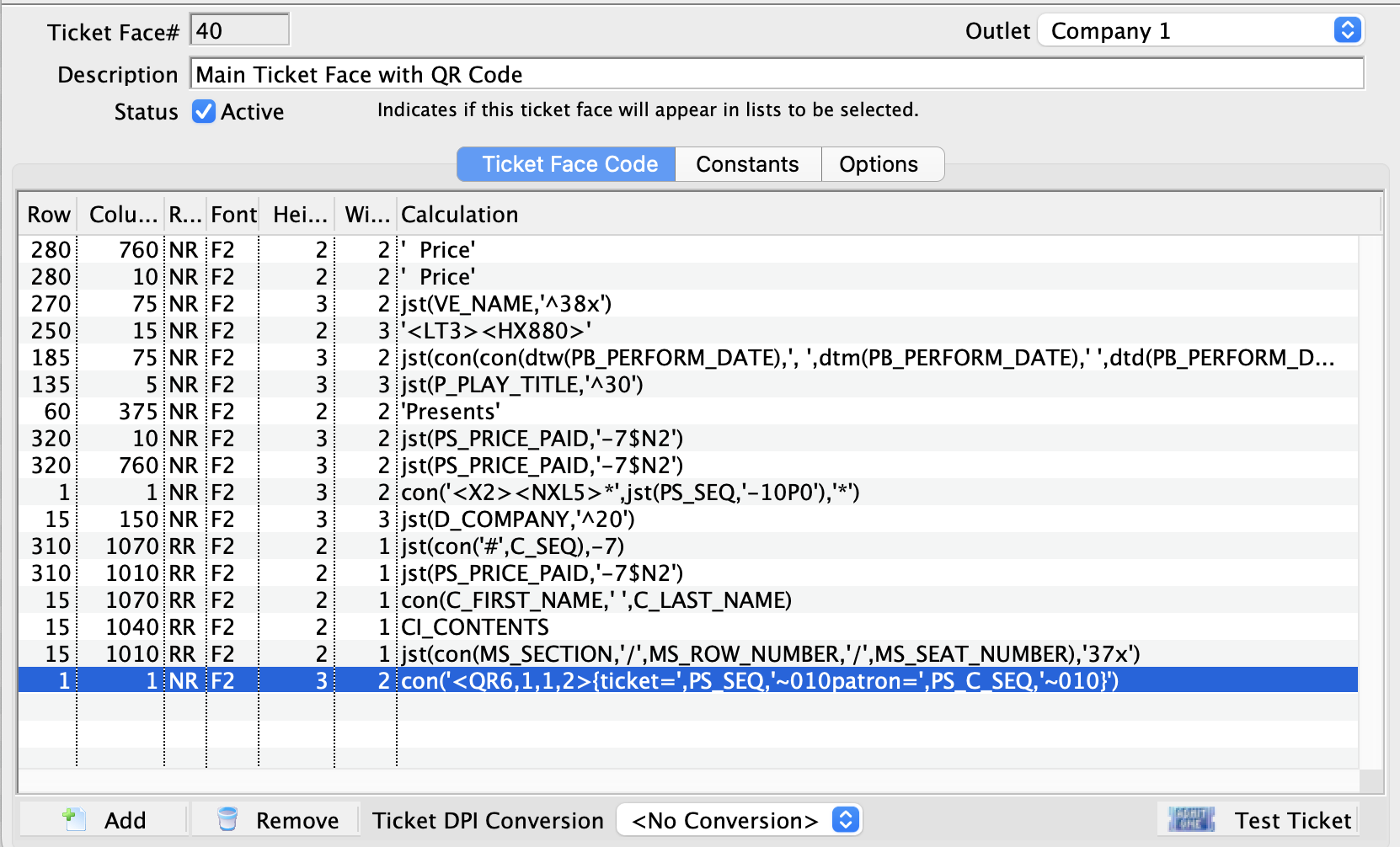
- Double-click to open this line of code.
-
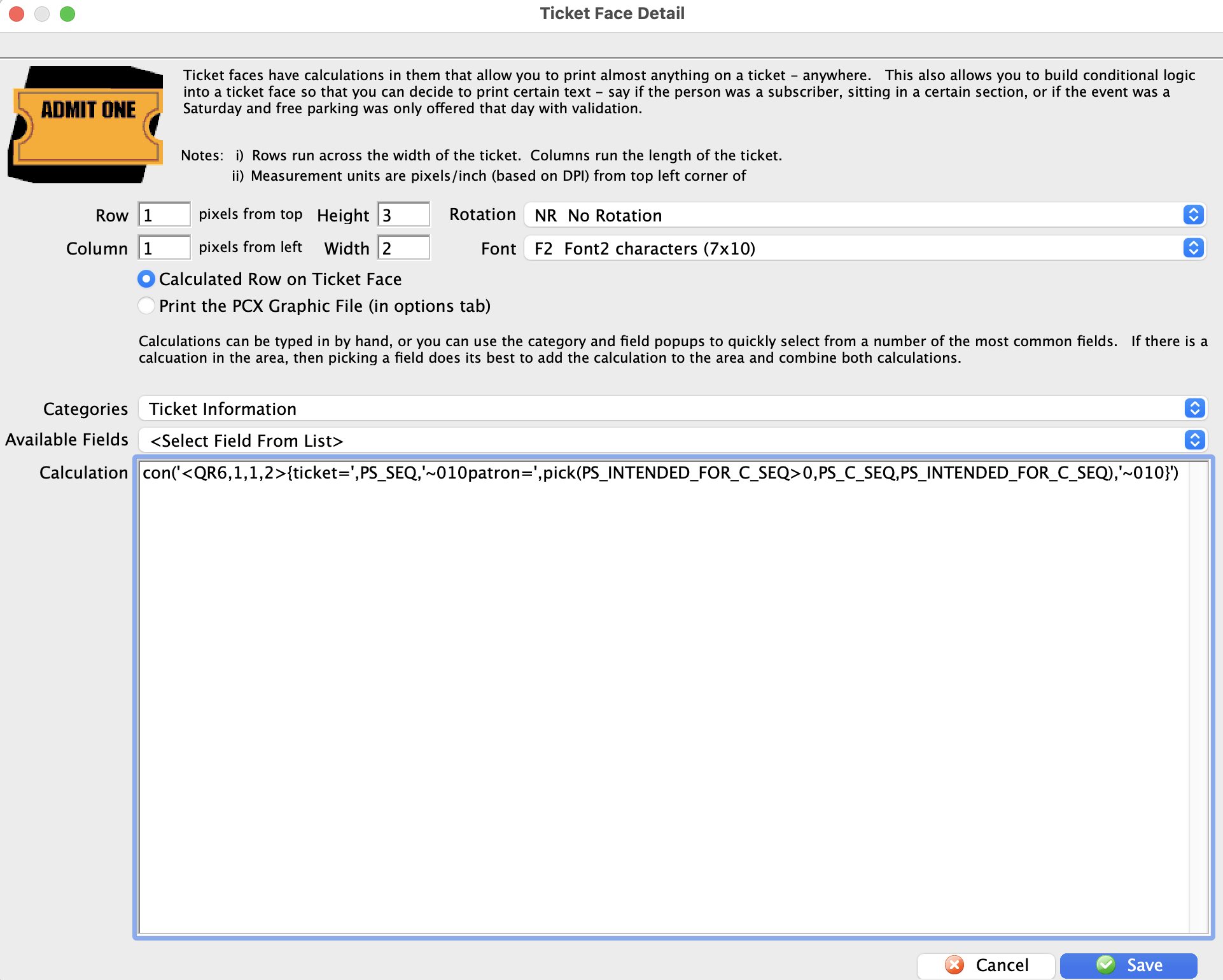
Replace the entire code with this updated version:
con('<QR6,1,1,2>{ticket=',PS_SEQ,'~010patron=',pick(PS_INTENDED_FOR_C_SEQ>0,PS_C_SEQ,PS_INTENDED_FOR_C_SEQ),'~010}')
Any tickets that have previously been Gifted and printed prior to updating the ticket face code can be unprinted and reprinted. This will ensure they can be scanned at the time of entry.
